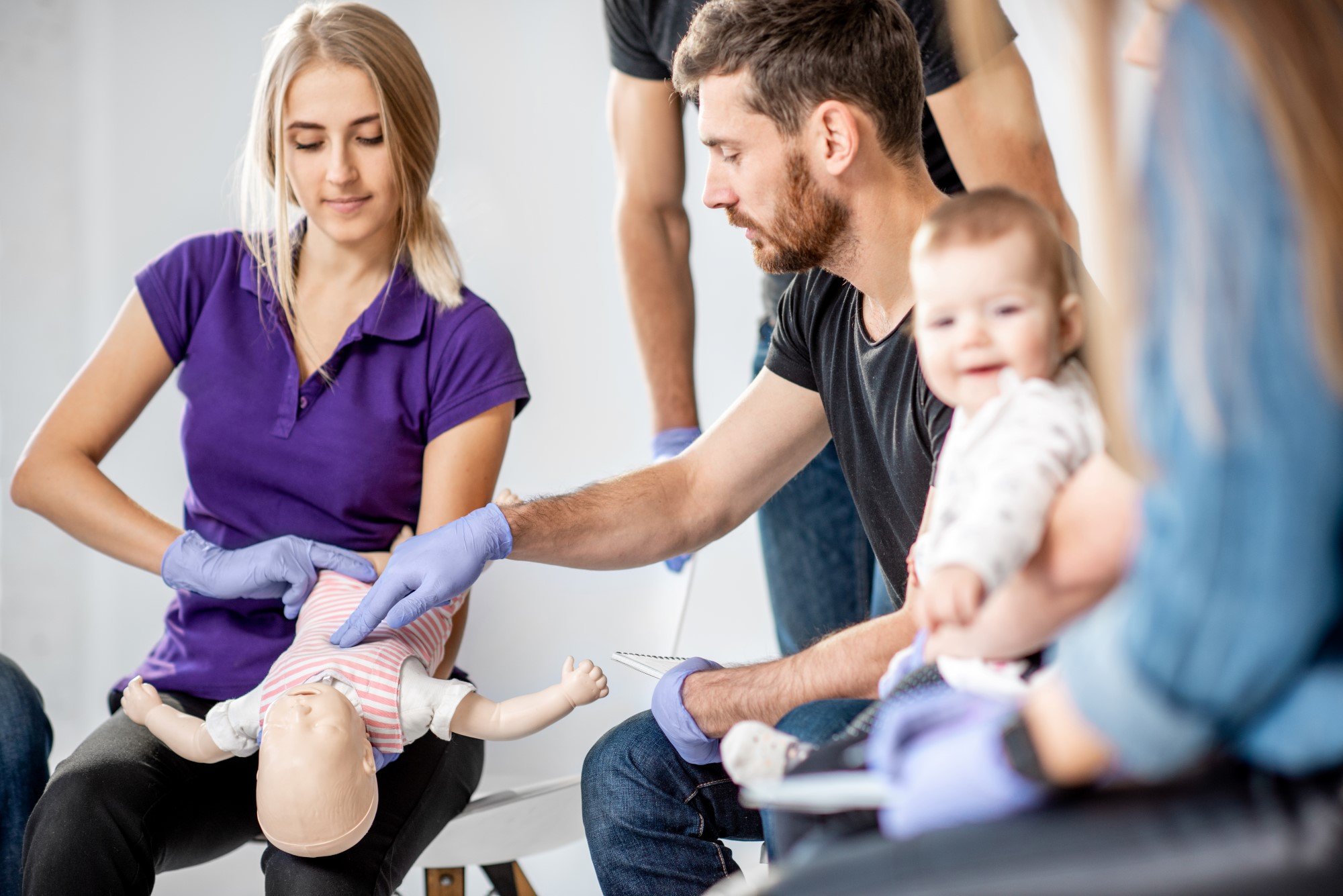
Few sounds are more alarming than that of a child who is choking. Understanding how to prevent choking, as well as what to do when choking occurs, can save your child’s life.
Nearly two thirds of children who choke to death are three years of age or younger. Most of these deaths can be avoided.
If a child is choking, first find out if the child can breathe, cry or speak. A strong cough generally means the airways is not completely blocked, and the child may be able to dislodge the blockage by coughing.
Only begin first aid if the child cannot breathe at all, or the child's airway is so blocked that there's only a weak cough and a loss of color.
Conscious Infant (Under one year old)
- Support head and neck with one hand. Place the infant face down over your forearm, head lower than torso, supported on your thigh.
- Deliver up to five back blows, forcefully, between the infant’s shoulder blades using the heel of your hand.
- While supporting the head, turn the infant face up, head lower than torso.
- Using two or three fingers, deliver up to five thrusts in the sternal (breastbone) region. Depress the sternum ½ to 1 inch for each thrust. Avoid the tip of the sternum.
- Repeat both back blows and chest thrusts until the foreign body is expelled or the infant becomes unconscious.
- Do not perform blind finger sweeps or abdominal thrusts on infants.
- Alternative method: Lay the infant face down on your lap, head lower than torso and firmly supported. Perform up to five back blows. Turn the infant on his or her back as a unit and perform up to five chest thrusts.
Unconscious Infant (Under one year old)
- Shout for help. Call 911 or the local emergency number.
- Perform the tongue-jaw lift. (Grip on the jaw by placing your thumb in the infant’s mouth and grasping the lower incisor teeth or gums; the jaw then lifts upward.) If you see the foreign body, remove it.
- If trained to do so, begin rescue breathing.
- Perform the sequence of back blows and chest thrusts as described for a conscious infant.
- After each sequence of back blows and chest thrusts, look for the foreign body and, if visible, remove it.
- Resume rescue breathing.
- Continue with the sequence of back blows and chest thrusts, and, after each sequence continue to check for the foreign body, which should be removed.
- If the foreign body is removed and the infant is not breathing, begin CPR.
Conscious Child (Over one year old)
- To dislodge an object from the airway of a child perform abdominal thrusts (the Heimlich Maneuver) as described for adults. Avoid being overly forceful in order to avert injury to ribs and internal organs (use your best judgment).
Unconscious Child (Over one year old)
- If the child becomes unconscious, continue as for an adult, except:
- Do not perform a blind finger sweep in children up to 8 years old. Instead, perform a tongue-jaw lift and remove the foreign body only if you can see it.
ACEP also provides information on how to perform CPR for an adult. CPR instructions for an adult.
 American College of Emergency Physicians
American College of Emergency Physicians